|
For the year ended 30 June 1999
Note 1: Reporting Entity and Objectives The reporting entity comprises the Department of the Treasury, the Foreign Investment Review Board, the Loan Council and the Royal Australian Mint (the Mint), hereafter referred to as The Department comprises two programs: Program 1: Treasury (including the secretariats of the Foreign Investment Review Board and the Loan Council). Program 2: Royal Australian Mint. The objectives of these programs are respectively: Program 1: To improve the wellbeing of the Australian community through high, sustainable economic and employment growth with low inflation and efficient and sustainable use of resources. Program 2: To produce and supply Australia Treasury is funded predominantly by Parliamentary appropriations. The Mint operates as a government business, and seeks to make a commercial return on investment. The financial report encompasses various trust accounts and all the Funds through which the Department controls resources to carry on its functions. In the process of reporting on the Department as a single entity all transactions and balances within that entity have been eliminated. Note 2: Summary of Significant Accounting Policies 2.1 Basis of Accounting The financial statements are required by section 49 of the Financial Management and Accountability Act 1997 and are a general purpose financial report. The financial statements have been prepared in accordance with Schedule 2 to the Financial Management and Accountability (FMA) Orders made by the Minister for Finance and Administration in December 1998. The financial statements have been prepared: The financial statements have been prepared on an accrual basis and in accordance with historical cost convention except for certain assets which, as noted, are at valuation. Except where stated, no allowance is made for the effect of changing prices on the results or the financial position. The continued existence of the Department in its present form, and with its present programs, is dependent on Government policy and on continuing appropriations by Parliament for the Department 2.2 Agency and Administered Items Agency assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses are those items that are controlled by the Department including: Administered items are those items which are controlled by the Government and managed or overseen by the Department on behalf of the Government. These items include grant payments to other governments, interest on public debt and dividend revenue from financial institutions. The purpose of the separation of administered and agency items is to enable assessment of the administrative efficiency of the Department in providing goods and services. The basis of accounting described in Note 2.1 applies to both agency and administered items. Administered items are distinguished from agency items in the financial statements by shading. 2.3 Changes in Accounting Policy Changes in accounting policy have been identified in this note under their appropriate headings. 2.4 Principles of Aggregation In the process of reporting the Department as a single unit, and in preparation of the program statements, all intra- and inter-program transactions and balances have been eliminated in full. The financial statements of the Mint are aggregated into the Department’s financial statements. Where accounting policies differ between the business operations and the Department, adjustments are made on aggregation to bring any dissimilar accounting policies into alignment. Administered investments in controlled entities are not consolidated on a line-by-line basis because their aggregation is relevant only on the Whole of Government level (see note 2.21). 2.5 Revenues from Government Revenues from government are revenues relating to the core operating activities of the Department, except to the extent that they represent the receipt of assets arising from a restructuring of administrative arrangements. Agency Appropriations Appropriations for agency operations other than running costs are recognised as revenue to the extent that the appropriations are spent. Appropriations for agency running costs have, until 1998-99, been recognised as revenue in the year of appropriation, except to the extent that: With the introduction of accrual budgeting by the Commonwealth for 1999-2000, any re-appropriation to the Department of the automatic running costs carryover for 1999-2000 will be by way of a capital rather than a revenue appropriation. Accordingly, the carryover is not recognised as revenue but is included directly in equity in the financial statements for 1998-99. Administered Appropriations Administered appropriations are recognised as revenue only to the extent that The amount of revenue is disclosed as ‘transfers – cash from Official Commonwealth Public Account’ and ‘Special Appropriations Accrued’ in the statement of Administered Revenues and Expenses. The ‘Special Appropriations Accrued’ gives rise to an Appropriation Receivable as disclosed in the statement of Administered Assets and Liabilities. Resources Received Free of Charge Services received free of charge are recognised in the statement of Agency Revenues and Expenses as revenue when and only when a fair value can be reliably determined and the services would have been purchased if they had not been donated. Use of those resources is recognised in the ‘Net cost of services’. 2.6 Other Revenue Revenue from the sale of goods is recognised upon the delivery of goods to customers. Interest revenue is recognised on a proportional basis taking into account the interest rates applicable to the financial assets. Dividend revenue is recognised when the right to receive a dividend has been established. Revenue from disposal of non-current assets is recognised when control of the asset is passed to the buyer. All revenues described in this note are revenues relating to the core operating activities of the Department, whether in its own right or on behalf of the Commonwealth, except for gains from the sale of agency assets. Details of revenue amounts are given in Note 7. 2.7 Grants (Administered) The Treasury Department administers a number of grant schemes on behalf of the Commonwealth. Grants are generally expensed when the payment is made. That is, there is no liability recognised. However, the Department recognises a liability for future grant payments to the International Monetary Fund (IMF) Enhanced Structural Adjustment Facility. In 1997-98, the Department of the Treasury agreed to contribute $30,000,000 in twelve annual installments of $2,500,000 to the IMF’s Enhanced Structural Adjustment Facility. The Department has made two payments and has a liability of $25,000,000.
2.8 Revenue Replacement Payments The Commonwealth collects a number of revenue replacement taxes as an agent for the States and Territories. These taxes have replaced constitutionally invalid business franchise fees and are passed directly by the Commonwealth to the State and Territory Governments, with an adjustment for administration costs. Reflecting the Commonwealth’s agency role in the collection of these taxes, they have not been recognised in these financial statements. Under the previous accounting policy, the revenue replacement payments were treated on a gross basis. The relevant amounts for 1997-98 and 1998-99 are outlined in the table below.
2.9 Mirror taxes collected by State and Territory Governments The Commonwealth imposes mirror taxes on behalf of the States which replace constitutionally invalid State taxes on Commonwealth places. Mirror taxes are collected by the States and will be passed to the Commonwealth and immediately repaid to the States. The State Governments bear the administration costs of collecting mirror taxes. There has to date been no mirror taxes paid to the Commonwealth by the States as not all States have yet passed legislation facilitating such payment. 2.10 Employee Entitlements
Leave The liability for employee entitlements includes provisions for annual leave and long service leave. No provision is made for sick leave as all sick leave is non-vesting and the average sick leave taken in future years by employees of the Department is estimated to be less than the annual entitlement for sick leave. The liability for annual leave reflects the value of total annual leave entitlements of all employees at 30 June 1999 and is recognised at the nominal amount. The non-current portion of the liability for long service leave is recognised and measured at the present value of the estimated future cash flows to be made in respect of all employees at 30 June 1999. In determining the present value of the liability, the Department has taken into account attrition rates and pay increases through promotion and inflation. Separation and Redundancy Provision is also made for separation and redundancy payments in circumstances where the Department has formally identified positions as excess to requirements and a reliable estimate of the amount of the payments can be determined. Superannuation Staff of the Department contribute to the Commonwealth Superannuation Scheme and the Public Sector Superannuation Scheme. Employer contributions amounting to $3,509,235 have been expensed in these financial statements. No liability is shown for superannuation in the statement of Agency Assets and Liabilities as the employer contributions fully extinguish the accruing liability, which is assumed by the Commonwealth. Employer Superannuation Productivity Benefit contributions totalled $680,005. 2.11 Leases A distinction is made between finance leases, which effectively transfer from the lessor to the lessee substantially all the risks and benefits incidental to ownership of leased non-current assets, and operating leases under which the lessor effectively retains substantially all such risks and benefits. Where a non-current asset is acquired by means of a finance lease, the asset is capitalised at the present value of minimum lease payments at the inception of the lease and a liability recognised for the same amount. Leased assets are amortised over the period of the lease. Lease payments are allocated between the principal component an Operating lease payments are charged to the statement of Agency Revenues and Expenses on a basis which is representative of the pattern of benefits derived from the leased assets. 2.12 Cash Cash includes notes and coins held, deposits held at call with a bank or financial institution and balances of commercial trust accounts held in the Official Commonwealth Public Account (CPA). 2.13 Financial Instruments and Specific Disclosures by Financial Institutions
The Department is complying with the requirements of the following Australian Accounting Standards: (a) AAS 23 Set-off and Extinguishment of Debt; (b) AAS 32 Specific Disclosures by Financial Institutions; and (c) AAS 33 Presentations and Disclosure of Financial Instruments. Where practicable, comparative information has been disclosed. Accounting policies for financial instruments are stated at notes 29 and 30A. 2.14 Acquisition of Assets Assets are recorded at cost on acquisition except as stated below. The cost of acquisition includes the fair value of assets transferred in exchange and liabilities undertaken. Assets acquired at no cost or for nominal consideration are initially recognised as assets and revenue at their fair value at the date of acquisition, unless acquired as a consequence of restructuring administrative arrangements. In the latter case, assets are initially recognised at the amounts at which they were recognised in the transferor agency’s accounts immediately prior to the restructuring. 2.15 Property Plant and Equipment
Asset Recognition Threshold Purchases of property, plant and equipment are recognised initially at cost in the statement of Agency Assets and Liabilities, except for purchases costing less than $2,000 which are expensed in the year of acquisition (other than where they form part of a group of similar items which are significant in total). Revaluation Schedule 2 of the FMA Orders requires that property, plant and equipment be progressively revalued in accordance with the ‘deprival’ method of valuation by 1 July 1999. Thereafter they are to be revalued progressively on that basis every three years. Revaluations of property, plant and equipment are accounted for by separately restating the gross amount and the related accumulated depreciation of the revalued asset. The carrying amounts of property, plant and equipment held by the Mint have been reviewed to determine whether they are in excess of their recoverable amounts. In assessing recoverable amounts the relevant cash flows have not been discounted to their present value. The Department is implementing its progressive revaluations as follows: Assets in each class acquired after the commencement of the progressive revaluation cycle will be reported on the basis of the value initially recognised on acquisition for the duration of the progressive revaluation then in progress. The financial effect of the move to progressive revaluation is that the carrying amounts of assets will reflect current values and depreciation charges will reflect the current cost of the service potential consumed in each period. Intangible Assets Where recognised, intangible assets are reported at the lower of cost, recoverable amount or valuation. They are amortised on a straight line basis over their anticipated useful lives. Depreciation and Amortisation Depreciable property, plant and equipment are written off to their estimated residual values over their estimated useful lives to the Department using the straight line method of depreciation. Leasehold improvements are amortised on a straight line basis over the lesser of the estimated useful life of the improvements or the unexpired period of the lease. Depreciation and amortisation rates applying to each class of depreciable assets are as follows:
Depreciation and amortisation rates and methods are reviewed at each balance date and necessary adjustments are recognised in the current and future reporting periods as appropriate. The aggregate amount of depreciation allocated for each class of asset during the reporting period is disclosed in Note 14B. 2.16 Inventories Inventories are brought to account at the lower of cost and net realisable value. Work in progress and finished goods are brought to account at actual costs to include direct costs and a proportion of direct labour and overhead. All precious metals are purchased and brought to account at cost and expensed as used. Indirect materials are expensed at the time of purchase. 2.17 Taxation The Department of the Treasury is exempt from all forms of taxation except for Fringe Benefits Tax. The Mint is liable for all forms of taxation including Payroll tax, Companies profit tax, fringe benefit tax and sales tax on non-coin products. 2.18 Insurance A new Commonwealth insurable risk managed fund called ‘Comcover’, commenced operations as from 1 July 1998. From that date, the Department has insured with the fund for risks other than workers compensation, which is dealt with via continuing arrangements with Comcare. The new arrangements replace the previous policy of non-insurance and require the systematic identification, quantification, reporting and management of risk across the department. 2.19 Bad and Doubtful Debts Bad debts are written off during the year in which they are identified to the extent to which they have not been provided for. A provision is raised for any doubtful debts based on a review of all outstanding accounts as at year end. 2.20 Comparative Figures Where necessary, comparative figures have been adjusted to conform to changes in presentation within these financial statements. 2.21 Statement of Significant Accounting Policies for Administered Items
Administered items include: Unclaimed Moneys Moneys from bank accounts inactive for seven years are transferred to the Commonwealth from banking institutions. These unclaimed moneys are deposited in the Consolidated Revenue Fund and are recognised as administered revenue. A provision representing the expected recovery of these moneys less refunds paid, based on an analysis of historical transactions, is recognised. Guarantees Guarantees provided under legislation within the portfolio responsibility of the Treasurer are recognised as liabilities when it is probable that the guarantee will be called and it can be reliably measured. In all other instances such guarantees are disclosed in statement of Administered Remote Contingencies (Note 16). State and Territory Advances Advances made to the States and Territories are recognised at their expected recoverable amount at balance date. Royal Australian Mint Seigniorage and Repurchase of Circulating Coins Seigniorage is collected by the Mint on behalf of the Commonwealth. Seigniorage represents the difference between the face value of coinage sold to the Reserve Bank of Australia and its cost of production to the Mint. The Mint repurchases circulating coins on behalf of the Commonwealth. The costs incurred by the Mint in repurchasing circulating coins are offset to an extent by the sale of scrap metal and the balance is supplemented by the Commonwealth via a reduction in the total amount paid to the Commonwealth by the Mint. Loan Consolidation and Investment Reserve The value of Commonwealth issued securities held in the Loan Consolidation and Investment Reserve is deducted from the face value of the administered borrowings liability. Any gain or loss on repurchase is reported in the statement of Administered Revenues and Expenses. The net effect is to report the impact of transactions with external parties. Reserve Bank of Australia Dividend In these accounts, the treatment of the Reserve Bank of Australia dividend has been changed, reflecting a change in the revenue recognition standard (AAS 15/AASB 1004) for 1998-99. This means that revenue, including dividends, can now only be brought to account once the right to control the income stream is established. On this basis, the RBA’s dividend for 1998-99 will be recognised in Treasury’s accounts in 1999-2000. An amount of $2,725,982,788 (Note 17) was received in 1998-99 representing the balance of the dividend receivable at 30 June 1998. Investments Development Banks Investments in development banks are classified as non-monetary assets. Where the information is available, these investments are recognised at historical cost. Where historical cost records are not readily obtainable, a notional cost has been established at 30 June 1993 by reference to the Development Banks The investment in the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) is recognised at historical cost, whereas the investments in the Asian Development Bank (ADB), the International Finance Corporation (IFC), the Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA) and the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) are recognised at notional cost. Owing to their nature, these investments are only revalued periodically. International Monetary Fund (IMF) The quota is the current value in Australian dollars of Australia The Special Drawing Rights (SDR) allocation liability reflects the current value in Australian dollars of the liability to repay to the IMF Australia Portfolio Agencies The Commonwealth’s investment in other controlled authorities and companies in this portfolio is valued at the aggregate of the Commonwealth’s share of the net assets and net liabilities of each entity as at 30 June 1997. Promissory Notes Promissory notes which have been issued in foreign currencies are translated at the spot rate at balance date. Foreign currency gains and losses are recognised where applicable. Promissory notes have been issued to the International Monetary Fund, International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, the Asian Development Bank and the Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency. Payments to the States Grants are recognised as expenses at the time that conditions under the grant agreement have been satisfied or payment has been made. Borrowings Borrowings are measured at face value. Premiums and discounts in relation to borrowings are netted and amortised over the life of the borrowings on a straight line basis. Borrowings are recognised on a gross basis, including borrowings on behalf of the State and Territory Governments. Receivables relating to borrowings on behalf of the State and Territory Governments are recognised as administered assets. Foreign Currency Transactions Transactions denominated in a foreign currency are converted at the exchange rate at the date of the transaction. Foreign currency receivables and payables are translated at the exchange rates current as at balance date. Where a purchase denominated in foreign currency is specifically hedg Derivative Transactions The Department undertakes derivative transactions on behalf of the Commonwealth to assist with the management of market risk associated with the Commonwealth debt portfolio. The Department manages this market risk by entering into interest rate swaps and cross-currency swaps. Swap principal associated with cross-currency swaps is recognised on a net basis using the cost method. The notional principal associated with interest rate swaps is not recognised as assets or liabilities. Swap interest payable and receivable in relation to interest rate and cross-currency swaps is also recognised on a net basis. Prior to 1997/98, swap contracts were recognised on a gross cost basis. Mortgage Insurance Policies Written by Housing Loans Insurance Corporation (HLIC) up to 12 December 1997 The HLIC was sold by the Commonwealth on 12 December 1997. Terms and conditions of the sale included that the Commonwealth shall remain responsible for the mortgage insurance policies written up to the time of the sale. The sale of the HLIC was conducted by the Office of Asset Sales and Information Technology Outsourcing. Accounting policies adopted are: Premiums Premiums comprise amounts charged to the policyholder or other insurer, excluding amounts collected on behalf of third parties, principally stamp duties. The earned portion of premiums received and receivable is recognised as revenue. Premiums are treated as earned from the date of attachment of risk. Premiums received in respect of insured loans are apportioned over a number of years in accordance with an actuarial determination of the pattern of risk in relation to the loans. Premium amounts carried forward in this way are credited to Claims Claims incurred expense and a liability for outstanding claims are recognised in respect of insurance policies. The liability is assessed on an actuarial basis and covers claims incurred but not yet paid, incurred but not yet reported and the anticipated direct and indirect costs of settling those claims. Acquisition Costs A portion of acquisition costs relating to unearned premium revenue is deferred in recognition that it represents future benefits. Deferred acquisition costs are amortised on an actuarial basis over the reporting periods expected to benefit from the expenditure. 2.22 Investment in Sydney 2000 Olympic Coin Program (STOCP)
General The Royal Australian Mint and the Perth Mint have formed a partnership to market and distribute Sydney 2000 Olympic Coins. This partnership will conclude in 2001 after the Sydney Olympics. The Royal Australian Mint The Sydney 2000 Olympic Coin Program consists of 28 base metal coins, 16 silver coins and 8 gold coins. Profit Distribution The distribution of any profit is made on the following basis:
Foreign Currency Hedge The STOCP entered into a foreign currency hedge (the hedge) on 25 June 1997 to the value of $US34 million for the purpose of reducing the risk of foreign currency exposure on overseas sales. The currency hedge matures on 31 December 2000 and is expected to cover all overseas revenues. At present the STOCP has a commitment to the hedge of $US26 million. The hedge has been accounted for in accordance with AAS 20 (Part A) 2.23 Rounding Amounts are rounded to the nearest $1,000 except in relation to the following items: It should be noted that in some cases totals may not add due to rounding. Note 3: Events Occurring After Balance Date
Note 4: Goods and Services Expenses
Note 5: Grants
Note 6: Extraordinary Items Note 6A: Restructuring
During the year, the Consumer Affairs Division was transferred to the Treasury Department. Assets with a gross value of $608,000 and a written down value of $184,000 were transferred during 1998-99. As a result of the restructuring of administrative arrangements the Treasury Department assumed responsibility on 21 October from Department of Industry Science & Resources. In respect of the programs assumed the following assets and liabilities were recognised at the date of transfer:
Note 6B: Capitalisation of Assets
The above amount represents the value of assets not capitalised in prior years. Note 7: Non-taxation Revenue
Note 8: Reconciliation of Revenues from Independent Sources
Note 9: Revenues from Government
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DOFA: Internal audit | — |
200 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DOFA: Payroll, accounting and printing | — |
15 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DOFA: Comcover premium | 60 |
— |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
293 |
534 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Note 10: Debt
|
|
||
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
$’000 |
$’000 |
|
|
|
||
| Note 10A: Leases | ||
| Finance Lease Commitments: | ||
| Not later than one year | 653 |
22 |
| Later than one year and not later than two years | 644 |
|
| Later than two years and not later than five years | 310 |
|
|
|
||
| Minimum lease payments | 1,607 |
22 |
| Deduct: future finance charges | (106) |
|
|
|
||
| Lease liability | 1,501 |
22 |
|
|
||
| Total Lease liability is represented by: | ||
| Current | 589 |
22 |
| Non-current | 912 |
|
|
|
||
| Lease liability | 1,501 |
22 |
|
|
||
| Note 10B: Government securities | ||
| Government securities: | ||
| Securities issued on behalf of the Commonwealth | 85,897,242 |
94,514,019 |
| Securities issued on behalf of the States and Territories | 1,796,458 |
1,890,552 |
|
|
||
87,693,700 |
96,404,571 |
|
| Unamortised net premiums on Commonwealth Government Securities on issue |
|
|
|
|
||
| Total government securities | 89,053,504 |
97,746,374 |
|
|
||
| Maturity schedule for government secur ities as at 30 June 1999 is as follows: |
||
| Payable: | ||
| within one year | 17,081,236 |
19,405,769 |
| in one to two years | 12,580,412 |
9,825,720 |
| in two to five years | 16,503,480 |
23,077,014 |
| in more than five years | 41,528,572 |
44,096,068 |
|
|
||
87,693,700 |
96,404,571 |
|
|
|
||
| Note 10C: Loans | ||
| Loans | 36,522 |
43,943 |
| IMF Promissory Notes | 4,310,199 |
3,480,020 |
|
|
||
4,346,721 |
3,523,963 |
|
|
|
||
| Maturity schedule for loans is as follows: | ||
| Payable: | ||
| within one year | 11,686 |
7,728 |
| in one to two years | 6,988 |
12,554 |
| In two to five years | 15,038 |
18,836 |
| in more than five years | 2,810 |
4,825 |
| IMF Promissory notes payable on demand | 4,310,199 |
3,480,020 |
|
|
||
4,346,721 |
3,523,963 |
|
|
|
||
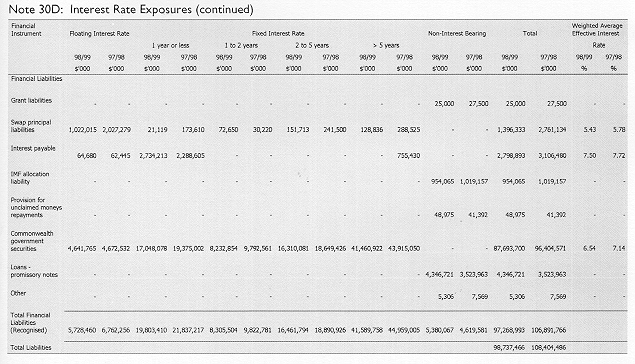
Note 11: Provisions and Payables
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
$’000 |
$’000 |
|
| Note 11A: Employee liabilities | ||
| Salaries and wages | 597 |
599 |
| Annual leave | 4,473 |
4,310 |
| Long service leave | 8,236 |
7,666 |
| Superannuation | 102 |
74 |
| Separation and redundancies | — |
93 |
| Total employee entitlement liability | 13,408 |
12,742 |
| Note 11B: Suppliers | ||
| Trade creditors | 1,126 |
1,044 |
| Total suppliers | 1,126 |
1,044 |
| Note 11C: Other | ||
| Other creditors | 4,965 |
1,110 |
| Unearned income | — |
37 |
| Total other | 4,965 |
1,147 |
| Note 11D: Grants | ||
| Grants – IMF – Enhanced Structural Adjustment Facility | 25,000 |
27,500 |
| Maturity schedule for grants is as follows: | ||
| Payable: | ||
| within one year | 2,500 |
2,500 |
| in one to two years | 2,500 |
2,500 |
| in two to five years | 7,500 |
7,500 |
| in more than five years | 12,500 |
15,000 |
25,000 |
27,500 |
|
| Note 11E: Payables due to other financial institutions | ||
| Swap principal | 1,396,333 |
2,761,134 |
| Swap interest | 10,501 |
22,493 |
| Total Payables | 1,406,834 |
2,783,627 |
| Maturity schedule for payables due to other financial institutions as at 30 June 1999 is as follows: | ||
| Payable: | ||
| within one year | 181,667 |
632,273 |
| in one to two years | 110,575 |
288,373 |
| in two to five years | 774,765 |
926,968 |
| in more than five years | 339,827 |
936,013 |
1,406,834 |
2,783,627 |
|
| NOTE 11F: Provisions and payables Other | ||
| Interest payable | 2,788,392 |
3,083,987 |
| IMF SDR allocation | 954,065 |
1,019,157 |
| Provisions for unclaimed moneys repayments | 48,975 |
41,392 |
| Provision for insurance claims | 20,894 |
29,533 |
| Provision for unearned premiums | 87,749 |
141,384 |
| Other | 5,332 |
7,569 |
| Total Other | 3,905,407 |
4,323,022 |
Note 12: Equity
|
|
|||||||||||
| Item | Accumulated results |
Asset revaluation reserve |
Total equity |
||||||||
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| Note 12A: Equity – Agency | |||||||||||
| Balance 1 July 1998 | 8,340 |
6,845 |
4,463 |
4,463 |
12,803 |
11,308 |
|||||
| Operating result | (3,049) |
1,495 |
— |
— |
(3,049) |
1,495 |
|||||
| Capitalisation of assets | 7,652 |
— |
— |
— |
7,652 |
— |
|||||
| Net asset revaluation reserve | — |
— |
1,210 |
— |
1,210 |
— |
|||||
| Carry forward appropriation | 3,763 |
— |
— |
— |
3,763 |
— |
|||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| Balance 30 June 1999 | 16,706 |
8,340 |
5,673 |
4,463 |
22,379 |
12,803 |
|||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| Note 12B: Equity – Administered | |||||||||||
| Balance 1 July 1998 | (92,453,310) |
(127,687) |
8,039,640 |
8,112,510 |
(84,413,670) |
7,984,823 |
|||||
| Net change in administered net assets | 10,186,896 |
8,769,984 |
— |
— |
10,186,896 |
8,769,984 |
|||||
| Net revaluation increase | — |
— |
— |
229 |
— |
229 |
|||||
| Net decrease in investment | — |
— |
— |
(73,099) |
— |
(73,099) |
|||||
| Change in accounting policy | — |
(101,095,607) |
— |
— |
— |
(101,095,607) |
|||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| Balance 30 June 1999 | (82,266,414) |
(92,453,310) |
8,039,640 |
8,039,640 |
(74,226,774) |
(84,413,670) |
|||||
|
|
|||||||||||
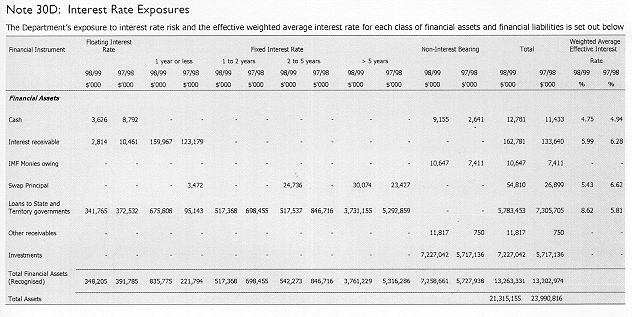
Note 13: Financial Assets
|
|
||
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
$’000 |
$’000 |
|
|
|
||
| Note 13A: Cash | ||
| Cash at bank and on hand | 547 |
36 |
|
|
||
| Note 13B: Receivables | ||
| Trade debtors | 1,007 |
1,414 |
| Other debtors | 3,802 |
3,856 |
| Less: Provision for Doubtful Debts | (77) |
(24) |
| Total receivables | 4,732 |
5,246 |
| Receivables (gross) are aged as follows: | ||
| Over due by: | ||
| Less than 30 days | 4,614 |
4,911 |
| 30 to 60 days | 84 |
133 |
| More than 60 days | 111 |
226 |
4,809 |
5,270 |
|
| Note 13C: Investments | ||
| RAM Interest in the STOCP at cost |
|
618 |
| RAM Interest in ITBs |
|
750 |
|
1,368 |
|
| Note 13D: Administered Financial Assets Cash | ||
| Cash at bank | 3,626 |
8,792 |
| Cash in trust accounts | 9,155 |
2,641 |
12,781 |
11,433 |
|
| Note 13E: Administered Financial assets Receivables due from other financial institutions |
||
| Swap principal | 54,810 |
26,899 |
| Swap interest | 93,557 |
62,120 |
| Total receivables | 148,367 |
89,019 |
| Maturity schedule for receivables due from other financial institutions as at 30 June 1999 is as follows: |
||
| Payable: | ||
| Within one year | 93,557 |
65,592 |
| In one to two years |
|
|
| In two to five years | 24,736 |
|
| In more than five years | 30,074 |
23,427 |
148,367 |
89,019 |
|
|
|
||
Note 13: Financial Assets (continued)
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
$’000 |
$’000 |
|
| Note 13F: Administered Financial assets Loans and advances |
||
| Loans to State and Territory governments | 5,783,453 |
7,305,705 |
| Less provision for doubtful debts |
|
|
| Total Loans and Advances | 5,783,453 |
7,305,705 |
| Maturity schedule for Loans to State and Territory governments as at 30 June 1999 is as follows: | ||
| Payable: | ||
| Within one year | 708,966 |
125,910 |
| In one to two years | 564,926 |
731,613 |
| In two to five years | 710,756 |
974,304 |
| In more than five years | 3,798,805 |
5,473,878 |
5,783,453 |
7,305,705 |
|
| Note 13G: Administered Financial assets Other receivables |
||
| Appropriation Receivable | 3,195,537 |
|
| APRA Supervisory levies | 11,106 |
|
| Profit transfer/Dividends owing |
|
2,726,000 |
| IMF related moneys owing | 10,647 |
7,411 |
| Interest receivable | 69,224 |
71,520 |
| Other | 711 |
1,136 |
| Total Other receivables | 3,287,225 |
2,806,067 |
| Note 13H: Administered financial assets Investments | ||
| International financial institutions | ||
| Asian Development Bank | 281,430 |
281,430 |
| European Bank for Reconstruction and Development | 51,486 |
51,486 |
| International Finance Corporation | 61,180 |
52,760 |
| International Bank for Reconstruction and Development | 265,082 |
265,082 |
| Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency | 5,819 |
|
664,997 |
650,758 |
|
| Quota | ||
| International Monetary Fund | 6,562,044 |
5,053,498 |
| Investment in Commonwealth entities | ||
| Reserve Bank of Australia | 8,035,041 |
8,035,041 |
| Australian Securities and Investments Commission | 4,267 |
4,267 |
| Companies and Securities Advisory Committee | 332 |
332 |
8,039,640 |
8,039,640 |
|
| Government securities | ||
| Internal Treasury Bills |
|
12,880 |
| Total investments | 15,266,681 |
13,756,776
|
Note 14: Non-financial Assets
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
$’000 |
$’000 |
|
| Note 14A: Infrastructure, plant and equipment | ||
| Computers, plant and equipment at valuation | 7,458 |
6,284 |
| Accumulated depreciation | (975) |
(2,220) |
6,483 |
4,064 |
|
| Computers, plant and equipment at cost | 3,124 |
6,842 |
| Accumulated depreciation | (1,247) |
(3,422) |
1,877 |
3,420 |
|
| Computers, plant and equipment under finance lease | 2,177 |
35 |
| Accumulated amortisation | (298) |
(13) |
1,879 |
22 |
|
| Leasehold improvements at valuation |
|
897 |
| Accumulated amortisation |
|
(732) |
|
165 |
|
| Leasehold improvements at cost | 414 |
910 |
| Accumulated amortisation | (77) |
(496) |
337 |
414 |
|
| Total infrastructure, plant and equipment | 10,576 |
8,085 |
| Intangibles | 8,135 |
787 |
| Accumulated amortisation | (630) |
(421) |
7,505 |
366 |
|
| Total infrastructure, Plant and Equipment and intangibles | 18,081 |
8,451 |
Note 14: Non-financial Assets (continued)
Note 14B: Analysis of Infrastructure, Plant, Equipment and Intangibles
Table A: Movement summary 1998-99 for all assets irrespective of valuation basis
| Item | Leasehold improvements |
Computers, plant |
Intangibles |
Total |
$’000 |
$’000 |
$’000 |
$’000 |
|
| Gross value as at 1 July 1998 | 1,807 |
13,159 |
787 |
15,753 |
| Additions | 221 |
3,779 |
7,510 |
11,510 |
| Disposals | (1,614) |
(1,134) |
(132) |
(2,880) |
| Revaluations |
|
(3,045) |
(30) |
(3,075) |
| Gross value as at 30 June 1999 | 414 |
12,759 |
8,135 |
21,308 |
| Accumulated depreciation/amortisation as at 1 July 1998 |
|
|
|
|
| Depreciation/amortisation charge for assets held 1 July 1998 |
|
|
|
|
| Depreciation/amortisation charge for additions |
|
315 |
|
|
| Adjustment for disposals | (1,497) |
(642) |
(133) |
(2,272) |
| Revaluations |
|
(4,144) |
(23) |
(4,167) |
| Accumulated depreciation/amortisation as at 30 June 1999 |
|
|
|
|
| Net book value as at 30 June 1999 |
|
|
|
|
| Net book value as at 1 July 1998 | 579 |
7,506 |
366 |
8,451 |
Table B: Summary of balances of assets at valuation as at 30 June 1999
| Item | Infrastructure, plant & equipment |
$’000 |
|
| As at 30 June 1999 | |
| Gross value | 7,458 |
| Accumulated depreciation/amortisation | (975) |
| Net book value | 6,483 |
| As at 30 June 1998 | |
| Gross value | 7,181 |
| Accumulated depreciation/amortisation | (2,952) |
| Net book value | 4,229 |
Note 14: Non-financial Assets (continued)
Note 14B: Analysis of Infrastructure, Plant, Equipment and Intangibles (continued)
Table C: Summary of balances of assets held under finance lease as at 30 June 1999
| Item | Computer, Plant & Equipment |
$’000 |
|
| As at 30 June 1999 | |
| Gross value | 2,177 |
| Accumulated depreciation/amortisation | (298) |
| Net book value | 1,879 |
| As at 30 June 1998 | |
| Gross value | 35 |
| Accumulated depreciation/amortisation | (13) |
| Net book value | 22 |
Note 14: Non-financial Assets (continued)
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
$’000 |
$’000 |
|
| Note 14C: Inventories | ||
| All Departmental inventories are current assets. | ||
| Raw materials | 7,031 |
3,559 |
| Work in progress (cost) | 1,281 |
165 |
| Finished goods (cost) | 4,881 |
2,238 |
| Total inventories | 13,193 |
5,962 |
| Note 14D: Other | ||
| Coin collection | 3,660 |
3,100 |
| Prepayments | 3,166 |
3,595 |
| Total other | 6,826 |
6,695 |
Note 15: Cash Flow Reconciliation
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
$’000 |
$’000 |
|
| Note 15A: Departmental reconciliation | ||
| Reconciliation of net cost of services to net cash provided by operating activities: |
||
| Net cost of services including business operations | (53,044) |
(49,227) |
| Revenue from government (Appropriation Receipts) | 50,799 |
50,250 |
| Abnormal item – Company profits tax (Royal Australian Mint) | (598) |
|
| Resources received free of charge | 293 |
534 |
| Extraordinary item restructuring | (499) |
(62) |
| Operating re sult |
(3,049) |
1,495 |
| Profit distribution | 618 |
(618) |
| Depreciation/amortisation | 2,407 |
2,143 |
| Asset write-off (Olympic Coin project costs) | 64 |
72 |
| Transfer of inventory to coin collection | 2 |
(4) |
| Loss of sale on disposal of infrastructure, plant and equipment |
556 |
|
| Profit on sale of infrastructure, plant and equipment |
|
(47) |
| Changes in assets and liabilities | ||
| Decrease in receivables | 943 |
(1,332) |
| Increase in other assets | (131) |
(2,273) |
| Increase in inventories | (7,231) |
(1,389) |
| Increase in employee liabilities | 666 |
(221) |
| Increase in suppliers | 82 |
(1,588) |
| Increase in other liabilities | 3,818 |
(32) |
| Increase in finance lease liability | 1,479 |
(46) |
| Asset adjustments |
|
(20) |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 224 |
(3,615) |
Note 15: Cash Flow Reconciliation (continued)
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
||
$’000 |
$’000 |
||
| Note 15B: Administered reconciliation | |||
| Reconciliation of net change in administered assets to net cash provided by operating activities: |
|||
| Net cost to government | (14,857,490) |
(21,678,093) |
|
| Cash from the Commonwealth Public Account - gross | 101,178,986 |
106,369,105 |
|
| Special Appropriation Accrued | 3,195,537 |
|
|
| Cash to the Commonwealth Public Account - gross | (79,330,137) |
(76,016,938) |
|
| Net revenue from extraordinary items |
|
95,910 |
|
| Net change in administered net assets | 10,186,896 |
8,769,984 |
|
| Cash from the Official Commonwealth Public Account | (74,512,272) |
(74,527,726) |
|
| Cash to the Official Commonwealth Public Account | 74,003,248 |
71,259,019 |
|
| Transfer of funds from Consolidated Revenue to Trust Fund | (8,544,540) |
(8,305,125) |
|
| Assumption of non cash assets of Housing Loans Insurance
Corporation |
|
|
|
| Assumption of liabilities of Housing Loans Insurance Corporation |
|
204,449 |
|
| Assumption of debt of Australian National Railways Commission | 230,101 |
460,812 |
|
| Waiver of debt - Victoria | 180,411 |
|
|
| Foreign exchange losses/(gains) | (586,197) |
2,698,393 |
|
| Amortisation of net premium on issue of debt | (281,139) |
(246,267) |
|
| Premium on redemption of debt | 508,127 |
1,302,973 |
|
| Other |
|
5,128 |
|
| Change in assets and liabilities: | |||
| (Increase)/decrease in dividend and interest receivables | 2,696,859 |
(724,379) |
|
| (Increase)/decrease in IMF remuneration receivables | (3,216) |
(5,467) |
|
| (Increase)/decrease in premiums receivable | 386 |
9,312 |
|
| (Increase)/decrease in appropriations receivable | (3,195,537) |
|
|
| (Increase)/decrease in other financial assets | (11,040) |
|
|
| (Increase)/decrease in non-financial assets | 9,631 |
7,173 |
|
| Increase/(decrease) in insurance claims and unearned premium provisions and payables |
(62,279) |
|
|
| Increase/(decrease) in unclaimed moneys provisions and payables |
7,583 |
|
|
| Increase/(decrease) in grant provisions and payables | (2,500) |
(2,500) |
|
| Increase/(decrease) in interest provisions and payables | (307,587) |
(743,464) |
|
| Increase/(decrease) in IMF provisions and payables | (2,263) |
1,806 |
|
| Net Cash from operating activities | 314,672 |
98,774 |
|
Note 16: Administered Remote Contingencies The following borrowings have been guaranteed by the Commonwealth in respect of authorities within the Treasury portfolio:
| Borrower | Legislation authorising guarantee |
Balance |
Balance |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
||
$’000 |
$’000 |
||
| Papua New Guinea | PNG Act 1949-75 & PNG Loans Guarantee Act 1975 |
|
|
| Commonwealth Bank of Australia (a) | CBA Act 1959 s117 | 94,124,900 |
99,745,900 |
| Commonwealth Bank of Australia Officers’ of Superannuation Fund (a) | CBA Act 1959 s117 |
|
|
| Commonwealth Development Bank (a) | CBA Act 1959 s117 | 272,600 |
472,500 |
| Reserve Bank of Australia (b) | RBA Act s77 | 38,160,000 |
34,755,086 |
| Housing Loans Insurance Corporation (c) | HLIC Act 1965 s30, 31(b) |
|
|
(a) In relation to the Commonwealth Bank of Australia, the Commonwealth Bank of Australia Officers’ of Superannuation Fund and the Commonwealth Development Bank, the Commonwealth guarantees all moneys that are, or may at any time become, payable to a person other than the Commonwealth. Such guarantee will be progressively phased out following the Government sell-down on 19 July 1996. (b) In relation to the Reserve Bank of Australia, the Commonwealth guarantees all moneys that are, or may at any time become, payable to a person other than the Commonwealth. (c) The HLIC was sold last year and residual contingencies have been assumed by the Commonwealth. The principal amount covered by the guarantee and the balances outstanding are unable to be reliably measured. The guarantee relates essentially to the Housing Loans Insurance Corporation’s (HLIC) contracts of mortgage insurance and any borrowings approved by the Treasurer up to 12 December 1997. (d) At the finalisation of these statements this figure was unavailable. Note 17: Receipts of the Consolidated Revenue Fund
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
| Receipts | |||
| Advances to the Australian Capital Territory Interest |
3,321,000 |
3,320,582 |
3,320,582 |
| Advances to the States under the Housing Agreements Interest |
142,818,000 |
133,121,241 |
145,687,049 |
| Advances to the Northern Territory for Housing Interest |
1,591,000 |
1,591,175 |
1,608,044 |
| Advances to the States under the Housing Assistance Act 1973 Interest |
200,000 |
188,201 |
203,438 |
| Advances to the States under the States (Works and Housing Assistance) Acts Interest |
93,627,000 |
88,184,418 |
94,395,361 |
| Advances to the States under the War Service Lands Settlements Acts Principal |
764,000 |
763,663 |
736,060 |
| Australian National Railways Commission
Debt repayment |
58,000,000 |
230,103,846 |
460,812,450 |
| Australian Prudential Regulation Authority Supervisory levies |
|
|
|
| Banking Act 1959 — Unclaimed moneys | 15,000,000 |
31,029,923 |
16,803,384 |
| Bank dividends | 2,600,000,000 |
2,725,982,788 |
1,700,000,000 |
| Borrowing levy and guarantee charge on borrowings by Commonwealth Government Enterprises |
|
|
5,256,153 |
| Fiscal contributions by State Government |
|
199,583,520 |
406,592,890 |
| Housing Loans Insurance Corporation — Dividend and special annual payment Payment of reserves to the Payment of balance liquidation |
|
|
|
| Interest paid by States and the Northern Territory on other loans |
|
|
566,898,890 |
| Interests on Financial Assets Remuneration |
214,000,000 |
|
|
Note 17: Receipts of the Consolidated Revenue Fund (continued)
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
| Loan management expenses — recoveries from the States and the Northern Territory |
75,000 |
44,289 |
81,570 |
| Loans Securities Amendment Act 1988 — receipts from swap counterparties |
5,550,000,000 |
5,035,530,178 |
3,277,578,379 |
| Loan to Papua New Guinea
Interest Principal |
|
|
3,578,426 69,400,000 |
| Loan to Brazil — Principal |
|
161,621,012 |
|
| Regulation of companies and securities | 326,863,000 |
331,778,258 |
326,015,066 |
| Royal Australian Mint and Coinage Trust Account — moneys in excess of requirements |
65,600,000 |
63,300,000 |
49,000,000 |
| Seigniorage payments Gold Corporation | 750,000 |
680,800 |
818,806 |
| Miscellaneous |
|
80,563 |
125,827 |
| Section 31 of the Financial Management and Accountability Act 1997 — to be credited to Running Costs — Division 670 |
991,000 |
653,045 |
928,913 |
| Total receipts | 9,573,948,000 |
10,585,572,647 |
7,489,439,992 |
Note 18: Expenditure from Special Appropriations
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
| Expenditure from Special Appropriations: | |||
| Airports (Transitional) Act 1996 — former debts of the Federal Airports Corporation — Interest |
51,900,000 |
52,457,364 |
51,133,618 |
| Commonwealth Inscribed Stock Act 1911, Loans Securities Act 1919, Loans Redemption & Conversion Act 1921 |
8,243,025,000 |
7,806,844,638 |
15,141,784,855 |
| Loans Securities Amendment Act 1988 payments to swap counterparties |
7,398,000,000 |
5,413,262,843 |
3,118,861,511 |
| Financial Agreement Act 1994 — Assistance for Debt Redemption |
28,100,000 |
81,692,916 |
62,265,944 |
| Loans Redemption and Conversion Act 1921 |
5,000 |
|
|
| Moomba — Sydney Pipeline System Sale Act 1994 |
19,070,000 |
19,061,690 |
18,936,779 |
| Financial Agreement Act 1994 — Commonwealth contribution to Debt Retirement Reserve Trust Account on State and Northern Territory Debt |
8,270,000 |
5,182,953 |
10,395,310 |
| Interest on Debt Retirement Reserve Trust Account Balances |
829,000 |
386,014 |
269,233 |
| Payment of Tax Receipt (Victoria) Act 1996 |
|
|
|
| States Grants (General Purposes) Act 1993 and 1994 |
23,237,843,000 |
23,702,792,607 |
21,783,582,539 |
| Asian Development Bank (Additional Subscription) Act 1995 |
2,352,000 |
2,686,812 |
2,424,381 |
| Banking Act 1959 | 15,000,000 |
10,569,949 |
10,006,817 |
| Commonwealth Inscribed Stock Act 1911, Treasury Bills Act 1914 — Payment of Special Bond premiums on redemption |
5,000 |
71 |
149 |
| Life Insurance Act 1995 | 1,200,000 |
2,700,000 |
|
| International Monetary Agreements Act 1947 |
522,695,000 |
1,264,716,623 |
726,603,211 |
| Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency Act 1996 |
|
2,909,680 |
|
| Qantas Sale Act 1992 — Qantas Debt S ervicing |
336,984,000 |
352,234,973 |
70,188,194 |
| Total expenditure from special appropriations |
39,865,278,000 |
38,717,499,133 |
40,996,452,541 |
Note 19: Expenditure from Annual Appropriations
|
|
||||||
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
| Ordinary Annual Services of Government Appropriation Act | Act No 1 |
Act No 3 |
$ |
$ |
$ |
$ |
|
|
||||||
| Division 670 – Administrative | ||||||
| 1 Running Costs | 52,921,045 |
2,362,000 |
|
55,283,045 |
54,944,631 |
50,555,856 |
| 2 Other Services | ||||||
01. Compensation and legal expenses |
943,000 |
|
|
943,000 |
350,065 |
112,748 |
| 02. Loan management expenses | 3,153,000 |
|
|
3,153,000 |
2,739,558 |
2,581,443 |
| 03. Overseas bond issues – Payments in respect of lapsed coupons |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 04. Australian National Railways Commission – Debt acquisition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 05. Proposed new Housing Loans Insurance Company – Payments in respect of insurance claims |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 06. International Finance Corporation – Capital subscription |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 07. International Bank for Reconstruction and Development – Capital subscription |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 08. Contributions to the International Monetary Fund - Enhanced Structural Adjustment Facility |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 09. Ex-Gratia payment to approved charitable organisations or trust funds in memory of the Princess of Wales |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Note: Budget estimates include section 31 deemed appropriation. Note 19: Expenditure from Annual Appropriations (continued)
|
|
||||||
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
| Ordinary Annual Services of Government Appropriation Act | Act No 1 |
Act No 3 |
$ |
$ |
$ |
$ |
|
|
||||||
| Division 673 – Australian Securities and Investments Commission | ||||||
| 01. For expenditure under the Australian Securities and Investments Commission Act 1989 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Division 674 – Companies and Securities Advisory Committee | ||||||
| 01. For expenditure under Part 9 of the Australian Securities and Investments Commission Act 1989 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Division 677 – Australian Prudential Regulation Authority | ||||||
| 1 Running Costs | 61,264,000 |
|
|
61,264,000 |
61,264,000 |
41,824,000 |
| 2 Other Services | ||||||
| 01. Compensation and legal expenses | 319,000 |
|
|
319,000 |
319,000 |
333,000 |
|
|
||||||
| Total – Appropriations Acts No 1 and 3 | 359,562,000 |
249,395,000 |
1,468,233 |
610,425,233 |
528,658,085 |
1,120,904,822 |
|
|
||||||
Note 19: Expenditure from Annual Appropriations (continued)
|
|
||||||
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
| Ordinary Annual Services of Government Appropriation Act | Act No 1 |
Act No 3 |
$ |
$ |
$ |
$ |
|
|
||||||
| Division 976 – Capital Works and Services | ||||||
| 1 Australian Securities and Investments Commission | ||||||
| For expenditure under the Australian Securities and Investments Commission Act 1989 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Division 977 – Payments to or for the States, the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory | ||||||
| 01. Australian Capital Territory – Special revenue assistance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 02. Companies and securities regulation – Compensation for loss of revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 04. Payments to State Governments in lieu of stamp duty on airport sales |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Division 978 – Other Services | ||||||
| 01. Community education and information program on the tax system |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
| Total – Appropriations Acts No 2 and 4 | 159,805,000 |
19,443,000 |
|
179,248,000 |
171,280,103 |
267,286,154 |
|
|
||||||
Note 20: Reconciliation of Agency Running Costs
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
|
| Running cost appropriation spent (Div 670-1) | 54,944,631 |
50,555,856 |
| Less: appropriation under the FMA Act section 31 | (653,044) |
(928,913) |
54,291,587 |
49,626,943 |
|
| Add carryover 30 June |
|
3,843,057 |
| Less carryover 1 July | (3,843,057) |
3,333,170 |
(3,843,057) |
509,887 |
|
| Revenue from Government (per operating statement) | 50,448,530 |
50,136,830 |
Note 21: Receipts and Expenditure of the Commercial Activities, Reserved Money Fund and Special Public Money
Loan Fund
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
|
| Receipts and Payments of Loan Fund | ||
| Receipts | ||
| Treasury Bonds | 3,896,387,000 |
4,503,634,000 |
| Treasury Notes | 45,064,391,363 |
50,631,650,942 |
| Treasury Bills – Internal | 18,935,000,000 |
11,895,600,000 |
| Treasury Indexed Bonds | 550,300,000 |
695,727,157 |
| Treasury (Adjustable Rate) Bonds |
|
|
| Premiums on issue of Commonwealth Securities | 299,139,229 |
801,815,117 |
| Total Loan Fund Receipts | 68,745,217,592 |
68,528,427,216 |
| Expenditure | ||
| Financial Agreement Act 1928, 1929,1944, 1966 and 1976 | ||
| Loan Flotation Expenses | 120,974 |
121,046 |
| Loans Redemption and Conversion Act 1921 | ||
| Treasury Notes | 48,282,258,502 |
53,540,947,994 |
| Australian Savings Bonds | 378,300 |
342,400 |
| Special Bonds | 2,360 |
3,670 |
| Treasury (Adjustable Rate) Bonds | 120,782,630 |
3,697,602,779 |
| Foreign currency redemptions | 212,151,916 |
230,619,753 |
| Other | 28 |
318 |
| Treasury Bonds | 7,596,839,204 |
4,768,015,625 |
| Treasury Bills Internal | 11,895,600,000 |
1,463,000,000 |
| Premiums on redemptions Treasury Bonds | 324,419,659 |
301,785,571 |
| Premiums on redemptions Treasury (adjustable rate) Bonds | 80,015,508 |
23,434,902 |
| Discount on redemptions Foreign currency | 931,576 |
744,414 |
| Total redemptions | 68,513,379,683 |
64,026,497,424 |
| Total loan fund expenditure | 68,513,500,657 |
64,026,618,470 |
Note 21: Receipts and Expenditure of the Commercial Activities, Reserved Money Fund and Special Public Money (continued)
Other Trust Moneys
- Legal Authority - Financial Management and Accountability Act 1997, section 20.
- Purpose for the receipt of moneys temporarily held in trust for other persons.
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Budget |
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
$ |
|
| Balance at beginning of reporting period | 13,000 |
13,000 |
13,000 |
| Receipts | 2,000 |
|
|
| Expenditure | 2,000 |
|
|
| Balance at end of reporting period | 13,000 |
13,000 |
13,000 |
Investment Transactions Account
|
|
||
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
|
|
|
||
| Investment balance at beginning of reporting period | 10,000 |
|
| Purchase of investments |
|
10,000 |
| Realisation of investments | 10,000 |
|
|
|
||
| Invested balance at end of reporting period |
|
10,000 |
|
|
||
| Cash balance at end of reporting period | 13,000 |
3,000 |
|
|
||
Note 21: Receipts and Expenditure of the Commercial Activities, Reserved Money Fund and Special Public Money (continued) Services for other government and non-departmental bodies
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Budget |
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
$ |
|
| Balance at beginning of reporting period | 19,463 |
19,463 |
13,301 |
| Receipts | 402,000 |
514,041 |
333,550 |
| Expenditure | 402,000 |
448,181 |
327,388 |
| Balance at end of reporting period | 19,463 |
85,323 |
19,463 |
Investment Transactions Account
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
|
| Investment balance at beginning of reporting period | 10,000 |
|
| Purchase of investments |
|
10,000 |
| Realisation of investments | 10,000 |
|
| Invested balance at end of reporting period |
|
10,000 |
| Cash balance at end of reporting period | 85,323 |
9,463 |
Note 21: Receipts and Expenditure of the Commercial Activities, Reserved Money Fund and Special Public Money (continued) Lloyds Deposit Trust Fund
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Budget |
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
$ |
|
| Balance at beginning of reporting period | 564,000 |
564,000 |
564,000 |
| Receipts |
|
3,330 |
|
| Expenditure |
|
|
|
| Balance at end of reporting period | 564,000 |
567,330 |
564,000 |
Investment Transactions Account
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
|
| Investment balance at beginning of reporting period | 564,000 |
564,000 |
| Purchase of investments | 567,330 |
|
| Realisation of investments | 564,000 |
|
| Invested balance at end of reporting period | 567,330 |
564,000 |
| Cash balance at end of reporting period |
|
|
Investments The balance of investments at 30 June 1999 includes the following investments held in the corporate name of the Treasurer of the Commonwealth pursuant to subsection 93(1) of the Insurance Act 1973 on behalf of the Trust.
| Rate of Interest
% |
Date of Maturity |
Face Value of Investment $ |
Cost of Investment $ |
| 9.5 | 31 March 2002 |
500,000 |
567,330 |
Note 21: Receipts and Expenditure of the Commercial Activities, Reserved Money Fund and Special Public Money (continued) Services for other government and non-departmental bodies
Australian Securities and Investments Commission
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Budget |
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
$ |
|
| Balance at beginning of reporting period | 668,595 |
668,595 |
157,702 |
| Receipts | 69,300,000 |
66,224,203 |
64,124,315 |
| Expenditure | 69,300,000 |
66,129,648 |
63,613,422 |
| Balance at end of reporting period | 668,595 |
763,150 |
668,595 |
Investment Transactions Account
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|||
Actual |
Actual |
|||
$ |
$ |
|||
| Investment balance at beginning of reporting period | 660,000 |
|
||
| Purchase of investments |
|
660,000 |
||
| Realisation of investments | 660,000 |
|
||
| Invested balance at end of reporting period |
|
660,000 |
||
| Cash balance at end of reporting period | 763,150 |
8,595 |
||
Note 21: Receipts and Expenditure of the Commercial Activities, Reserved Money Fund and Special Public Money (continued) Revenue Replacement Payments
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Budget |
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
$ |
|
| Receipts from CRF | 6,480,002,000 |
6,751,952,078 |
5,217,767,098 |
| Payments to States and Territories | 6,480,002,000 |
6,751,952,078 |
5,217,767,098 |
| Balance at end of reporting period |
|
|
|
| Accrued Liability due to adjustments |
|
27,101,556 |
|
Note 21: Receipts and Expenditure of the Commercial Activities, Reserved Money Fund and Special Public Money (continued) Trustee Companies (ACT) Deposits Trust Fund
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Budget |
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
$ |
|
| Balance at beginning of reporting period | 123,791 |
123,791 |
121,213 |
| Receipts |
|
572 |
32,993 |
| Expenditure |
|
|
30,415 |
| Balance at end of reporting period | 123,791 |
124,363 |
123,791 |
Investment Transactions Account
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Budget |
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
$ |
|
| Invested Balance at beginning of | |||
| Reporting period | 123,591 |
123,591 |
121,013 |
| Purchase of investment |
|
21,124 |
32,993 |
| Realisation of investment |
|
20,352 |
30,415 |
| Invested balance at end of reporting period |
|
124,363 |
|
| Cash balance at end of reporting period |
|
|
|
Investments The balance of investments at 30 June 1999 includes the following investments held in the corporate name of the Treasurer of the Commonwealth pursuant to subsection 10 (1) of the Trustee Companies Ordinance 1947 on behalf of the Trust.
Rate of Interest |
Date of Maturity |
Face Value of Investment |
Cost of Investment |
% |
$ |
$ |
|
| 7.0 | April 2000 | 20,000 |
21,124 |
| 7.0 | April 2000 | 20,000 |
19,999 |
| 10.0 | October 2002 | 20,000 |
20,599 |
| 9.5 | August 2003 | 10,000 |
12,119 |
| 7.5 | July 2005 | 30,000 |
30,313 |
| 7.5 | July 2005 | 20,000 |
20,209 |
Total |
120,000 |
124,363 |
|
Note 21: Receipts and Expenditure of the Commercial Activities, Reserved Money Fund and Special Public Money (continued) Royal Australian Mint and Coinage Trust Account
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Budget |
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
$ |
|
| Balance at beginning of reporting period | 759,241 |
759,241 |
6,028,893 |
| Receipts | 79,000,000 |
78,379,679 |
58,984,306 |
| Expenses | 79,000,000 |
78,637,934 |
64,253,958 |
| Balance at end of reporting period | 759,241 |
500,986 |
759,241 |
Investment Transactions Account
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
|
| Investment balance at beginning of reporting period | 750,000 |
|
| Purchase of investments |
|
750,000 |
| Realisation of investments | 750,000 |
|
| Invested balance at end of reporting period |
|
750,000 |
| Cash balance at end of reporting period | 500,986 |
9,241 |
Note 21: Receipts and Expenditure of the Commercial Activities, Reserved Money Fund and Special Public Money (continued) Debt Retirement Reserve Trust Account
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Budget |
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
$ |
|
| Balance at beginning of reporting period | 12,880,608 |
12,880,608 |
5,210,334 |
| Receipts | 76,112,000 |
61,565,464 |
2,045,394,033 |
| Expenses | 67,724,000 |
67,314,152 |
2,037,723,759 |
| Balance at end of reporting period | 21,268,608 |
7,131,920 |
12,880,608 |
Investment Transactions Account
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
|
| Investment balance at beginning of reporting period | 12,880,000 |
|
| Purchase of investments |
|
12,880,000 |
| Realisation of investments | 12,880,000 |
|
| Invested balance at end of reporting period |
|
12,880,000 |
| Cash balance at end of reporting period | 7,131,920 |
608 |
Note 21: Receipts and Expenditure of the Commercial Activities, Reserved Money Fund and Special Public Money (continued) Loan Consolidation and Investment Reserve Trust Account
1998-99 |
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Budget |
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
$ |
|
| Balance at beginning of reporting period | 12,221,183,774 |
12,221,183,774 |
3,827,132,114 |
| Receipts | 372,200,000 |
8,869,739,812 |
8,398,067,144 |
| Expenses |
|
5,111,041 |
4,015,484 |
| Balance at end of reporting period | 12,593,383,774 |
21,085,812,545 |
12,221,183,774 |
Investment Transactions Account
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Actual |
Actual |
|
$ |
$ |
|
| Invested balance at beginning of reporting period | 12,218,735,086 |
1,527,178,532 |
| Purchase of investment | 17,402,897,030 |
12,172,495,623 |
| Realisation of investment | 8,537,842,808 |
1,480,939,069 |
| Invested balance at end of reporting period | 21,083,789,308 |
12,218,735,086 |
| Cash balance at end of reporting period | 2,023,236 |
2,448,688 |
Note 21: Receipts and Expenditure of the Commercial Activities, Reserved Money Fund and Special Public Money (continued) Investments The balance of investments at 30 June 1999 includes the following investments in Commonwealth Government Inscribed Stock held in the corporate name of the Treasurer of the Commonwealth pursuant to sub section 6(3) of the Loan Consolidation and Investment Reserve Act 1955.
Rate of |
Date of |
Face Value of |
Cost of |
|
% |
$ |
$ |
||
| Treasury Fixed Coupon Bonds |
||||
| 13.00 | 15 Feb 00 | 123,685,000 |
143,480,802 |
|
| 13.00 | 15 May 00 | 69,261,148 |
80,611,986 |
|
| 7.00 | 15 Feb 01 | 42,556,200 |
44,083,823 |
|
| 10.00 | 15 Oct 02 | 885,000,000 |
1,041,068,327 |
|
| 5.25 | 15 July 03 | 27,123,600 |
25,421,909 |
|
| 6.50 | 15 July 03 | 1,563,700 |
1,611,300 |
|
| 5.40 | 15 May 04 | 10,500 |
8,478 |
|
| 9.00 | 15 Sept 04 | 760,000,000 |
889,372,140 |
|
| 6.00 | 15 July 05 | 9,528,000 |
9,572,822 |
|
| 7.00 | 15 July 05 | 2,000 |
1,927 |
|
| 10.00 | 15 Feb 06 | 2,057,890,000 |
2,625,446,077 |
|
3,976,620,148 |
4,860,649,591 |
|||
| Internal Treasury Bills | ||||
| 1.00 | 30 Jun 2000 | 16,205,000,000 |
16,205,000,000 |
|
| Total Australian Dollar Denominated Securities |
|
|
||
| Dutch Guilder Loans(a) | ||||
| 8.25 | 1 Nov 1999 | 11,126,841 |
10,079,810 |
|
| 7.25 | 1 Jan 2001 | 9,857,722 |
8,059,907 |
|
| Total Foreign Currency Denominated Securities |
|
|
||
| Total investments | 20,202,604,711 |
21,083,789,308 |
||
(a) Converted at $A=NLG 1.4057 Note 22: Appropriation for Future Reporting Periods The following table summarises appropriations for the 1999-00 financial year at 30 June 1999:
1999-2000 |
1998-99 |
|
$ |
$ |
|
| Special Appropriations | 26,713,062,000 |
38,717,499,133 |
| Appropriation Act No 1 Note (a) | 99,678,000 |
528,658,085 |
| Appropriation Act No 2 Note (a) | 238,012,000 |
171,280,103 |
27,050,752,000 |
39,417,437,321 |
|
Note (a): Appropriations for 1998-99 include Appropriations Acts No. 3 & 4. Note 23: Related Party transactions The related party transactions with STOCP are as follows:
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
$’000 |
$’000 |
|
| Sale of goods and services | ||
| coin sales | 2,670 |
2,080 |
| Other income | ||
| profit share | 1,183 |
618 |
| administration fee | 357 |
357 |
| Expenditure paid on behalf of the STOCP that has been or is to be reimbursed |
|
|
| Receivables | ||
| coin sales | 177 |
196 |
| administration fee | 89 |
89 |
| reimbursable expenditure | 149 |
266 |
Note 24: Payments to the Commonwealth from Business Operations
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
$’000 |
$’000 |
|
| Seigniorage | 63,980 |
47,434 |
| Royalty on Numismatic Coin Sales | 801 |
756 |
| STOCP royalty to Treasury | 1,850 |
763 |
| Loss from withdrawn circulating coin | (780) |
(458) |
| Trust Fund surplus | (3,503) |
321 |
| Prior year adjustment to seigniorage | 952 |
184 |
| Actual surplus funds paid to the Commonwealth | 63,300 |
49,000 |
Note 25: Executive Remuneration The number of executive officers that received or were due to receive total remuneration of $100,000 or more:
|
|
||
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Number |
Number |
|
|
|
||
| $100,000 to $110,000 | 4 |
15 |
| $110,001 to $120,000 | 5 |
14 |
| $120,001 to $130,000 | 15 |
4 |
| $130,001 to $140,000 | 3 |
2 |
| $140,001 to $150,000 | 3 |
3 |
| $150,001 to $160,000 |
|
1 |
| $160,001 to $170,000 | 2 |
|
| $170,001 to $180,000 | 2 |
|
| $180,001 to $190,000 | 1 |
|
| $230,001 to $240,000 |
|
1 |
| $240,001 to $250,000 |
|
|
| $260,001 to $270,000 |
|
1 |
| $280,001 to $290,000 | 1 |
|
|
|
||
36 |
41 |
|
| The aggregate amount of total remuneration of executive officers shown above |
|
|
| The aggregate amount of performance pay paid during the year to executive officers shown above |
|
|
| The aggregate amount of separation and redundancy payments to the executive officers shown above |
|
$82,120 |
|
|
||
The definition of executive officer in the FMO effectively requires the number of qualifying positions to be reported, rather than individuals (ie individuals were not necessarily remunerated at the levels shown). This means that the remuneration for each position will reflect that of the substantive occupant and any officers who acted in the position. Total remuneration includes actual salary, higher duties allowance, part day travelling allowance, employer superannuation component, separation and redundancy payments and an estimate of the non-salary component of the SES package. In light of changes to SES salary arrangements resulting from the Treasury Certified Agreement, it was decided that no payment of performance based pay would be made for the cycle payable in 1998-99. Note 26: Services Provided by the Auditor-General Financial statement audit services are provided free of charge to the Department. The trust account business, Royal Australian Mint, is required to remit an amount equivalent to the cost of its audit into the Consolidated Revenue Fund. The fair value of audit services provided was:
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
$ |
$ |
|
| Royal Australian Mint | 60,000 |
70,000 |
| Treasury | 215,000 |
200,000 |
275,000 |
270,000 |
|
No other services were provided by the Auditor-General. Note 27: Act of Grace Payments, Waivers and Amounts Written Off
|
|
||
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
$ |
$ |
|
|
|
||
| Agency
No Act of Grace payments were made during the reporting period |
||
| No waivers of amounts owing to the Commonwealth were made pursuant to subsection 34(1) of the Financial Management and Accountability Act 1997 | ||
| Amounts written off in accordance with subsection 47 (1) of the Financial Management and Accountability Act 1997 | ||
| Theft of cash advance for travel |
|
4,279 |
|
|
||
|
|
||
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
$ |
$ |
|
|
|
||
| Administered Waivers Waivers of amounts owing to the Commonwealth were made pursuant to subsection 70C(2) of the Audit Act 1901. These were amounts payable by South Australia in relation to Commonwealth advances under the States (Works and Housing) Assistance Acts and Commonwealth-State Housing Agreements. |
|
328,938,649 |
| Waivers of amounts owing to the Commonwealth were made pursuant to subsection 70C(2) of the Audit Act 1901. These were amounts payable by Victoria in relation to Commonwealth advances under the States (Works and Housing) Assistance Acts and Commonwealth-State Housing Agreements. | 180,411,000 |
|
|
|
||
Note 28: Average Staffing Levels Average staffing levels by program and in total were as follows
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|
Number |
Number |
|
| Program 1: Treasury | 498 |
480 |
| Program 2: Royal Australian Mint | 121 |
127 |
| Total | 619 |
607 |
Note 29: Financial Instruments Departmental
| Financial Instruments | Notes |
Accounting Policies and Methods (including recognition criteria and measurement basis) |
Nature of underlying instruments (including significant terms and conditions affecting the amount, timing and certainty of cash flows) |
| Financial Assets | Financial assets are recognised when control over future economic benefits is established and the amount of the benefit can be reliably measured. | ||
| Cash at bank | Deposits are recognised at their nominal amounts. Cash is received during day-to-day operations by the Collector of Public Money. | The Department of Treasury maintains a bank account with the Reserve Bank of Australia for the administration of petty cash and for the receipt and payment of moneys. The Royal Australian Mint maintains its own commercial accounts for the conduct of its business operations. | |
| Receivables for goods and services | These receivables are recognised at the nominal amounts due less any provision for bad and doubtful debts. Collectability of debts is reviewed at balance date. Provisions are made when collection of the debt is judged to be less rather than more likely. | Credit sales are normally on 30 day terms. | |
| Investments | The Royal Australian Mint and the Perth Mint have formed a partnership to market and distribute Sydney 2000 Olympic Coins. The Royal Australian Mint’s 50 per cent interest in the STOCP is carried at the recoverable amount. | The terms of the partnership are that any annual surplus will be retained in the partnership unless unanimously agreed by the partners. | |
| Financial Liabilities | Financial liabilities are recognised when a present obligation to another party is entered into and the amount of the liability can be reliably measured. | ||
| Trade creditors and accruals | (a) |
Creditors and accruals are recognised at their nominal amounts, being the amounts at which the liabilities will be settled. Liabilities are recognised to the extent that the goods or services have been received (and irrespective of having been invoiced). | Trade liabilities are normally settled on 30 day terms. |
| Finance lease liabilities | Liabilities are recognised at the present value of minimum lease payments at the beginning of the lease. The discount rates used are estimates of the interest rates implicit in the leases. | 1998-99 is the final year of the lease and covers the lease of three photocopiers. |
(a) Credit Risk: The maximum exposure to credit risk at the reporting date in relation to each class of recognised financial asset is the carrying amount of those assets as indicated in the balance sheet. The Department does not have any significant exposures to any concentrations of credit risk. The maximum value of credit risk exposure does not take into account the value of any collateral or other security.
Note 30: Financial Instruments Administered
Note 30A: Terms, Conditions and Accounting Policies
| Financial Instruments | Notes |
Accounting Policies and Methods | Nature of underlying instruments |
| Financial Assets | Financial assets are recognised when control over future economic benefits is established and the amount of the benefit can be reliably measured. | ||
| Cash at bank | Deposits are recognised at their nominal amounts. | The Department maintains two bank accounts with a commercial bank for the purposes of administering mortgage insurance policies written by the Housing Loans Insurance Corporation (HLIC) up to 12 December 1997 and a bank account for administering the wrap-up of the final accounts and other minor details up to the point of sale of the HLIC. | |
| Cash in trust accounts | Deposits are recognised at their nominal amounts. | The Department maintains two trust accounts within the Commonwealth Public Account. The Debt Retirement Reserve Trust Account (DRRTA) is held for the purposes of payment and receipt of moneys in relation to the redemption of Commonwealth Government Securities (CGS) on issue for the States and Territories. Interest earned is based on the RBA's Target Cash Rate and is paid monthly in arrears. Moneys are also held in the Loan Consolidation and Investment Reserve (LCIR) for the purpose of repurchase and redemption of CGS on behalf of the Commonwealth. Interest earned on the LCIR’s cash balances is included in the interest paid by the RBA to the Commonwealth on its overall cash balances. | |
| Interest and dividends receivable | Interest is credited to revenue as it accrues. Dividends from the Reserve Bank of Australia are recognised when determination is made by the Treasurer. | Interest is receivable on Commonwealth Government Securities, Swaps and other loans. The basis of payment of dividends is a memorandum of understanding with the Treasurer. |
Note 30A: Terms, Conditions and Accounting Policies (continued)
| Financial Instruments | Notes |
Accounting Policies and Methods | Nature of underlying instruments |
| International Monetary Fund moneys owing | Amounts owing from the International Monetary Fund are credited to revenue as they accrue. | Where the IMF’s holdings of Australian dollars fall below a specified level, it pays remuneration on Australia’s average remunerated reserve tranche position. The rate of remuneration is equal to the Special Drawing Rights (SDR) interest rate (this rate is then adjusted for burden sharing). Remuneration is calculated and paid at the end of the IMF’s financial quarters. | |
| Loans to State and Territory governments | Loans are recognised at the amounts lent. Interest is credited to revenue as it accrues. In relation to non Commonwealth Government Securities collectability of amounts outstanding is reviewed at balance date. Provision is made for bad and doubtful loans where collection of the loan or part thereof is judged to be less rather than more likely. In rare circumstances, loan repayments may be waived. | Until July 1990, the Commonwealth borrowed on behalf of the State and Territory Governments and allocated a portion of the proceeds of its Treasury Fixed Coupon Bond raisings to t hose Governments to fund the redemption of previous allocations of Commonwealth Government Securities (CGS). The States and Territories are responsible for meeting all obligations as to interest and principal on the CGS on allocation to them in accordance with the provisions of the Financial Agreement Act 1994. In addition to the CGS, there are outstanding balances of loans raised specifically for the States. State and Territory Government loans include advances, not evidenced by the issue of securities, made for housing and specific purpose capital payments. |
Note 30A: Terms, Conditions and Accounting Policies (continued)
| Financial Instruments | Notes |
Accounting Policies and Methods | Nature of underlying instruments |
| Swaps | (b) |
Swap principal associated with cross-currency swaps is recognised on a net basis using the cost method. Interest revenue and expense is recognised in the accounts as it accrues. The notional principal associated with interest rate swaps is not recognised as assets or liabilities. | The Treasury undertakes derivative transactions on behalf of the Commonwealth to assist with the management of market risk associated with the Commonwealth debt portfolio. The two main sources of market risk in respect of the Commonwealth debt portfolio are interest rate risk and exchange rate risk. The Treasury manages this market risk by managing the Commonwealth debt portfolio to a benchmark which reflects a portfolio composition that, ex ante, can be expected to minimise the cost of Commonwealth debt over the long term, subject to an acceptable degree of volatility in annual debt service costs. Derivative transactions offer a cost-effective means of managing the Commonwealth debt portfolio more closely in line with the benchmark than would otherwise be possible. Derivative transactions are currently limited to interest rate swaps and cross-currency swaps. |
| Investments Quota-International Monetary Fund | The investment is recognised as a monetary asset. It is denominated in Special Drawing Rights and is valued at the Australian dollar equivalent. Dividend income is not earned from this investment. | The Quota represents Australia’s membership subscription to the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Each member is required to pay to the IMF the amount of its initial quota and subsequent increases partly in the member’s own currency and the remainder in the form of reserve assets. A member’s quota is not increased until the member has consented to the increase. | |
| Investments International financial institutions | These investments are classified as non-monetary assets and recognised as at historical cost. Dividend income is not earned from these investments. | These investments represent Australia’s membership shareholding in the Asian Development Bank, the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, the International Finance Corporation and the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development. |
NOTES
b) Interest Rate Risk: The net fair values of cash and non-interest bearing monetary financial assets approximates their carrying value.
Note 30A: Terms, Conditions and Accounting Policies (continued)
| Financial Instruments | Notes |
Accounting Policies and Methods | Nature of underlying instruments |
| Financial Liabilities | Financial liabilities are recognised when a present obligation to another party is entered into and the amount of the liability can be reliably measured. | ||
| Grant liabilities | Grants are recognised as liabilities and expensed in the year in which the grant agreements are made. | This represents Australia’s contribution to the Enhanced Structural Adjustment Facility (ESAF) of the IMF. The ESAF will enable the IMF to provide concessional funding to support medium term macroeconomic adjustment and structural reforms in low income members of the IMF facing protracted balance of payment problems. The ESAF will assist Australia to promote its international economic and aid interests with developing countries in the Asian region. Australia’s contribution involves $30 million to be paid in annual instalments of $2.5 million over a 12 year period. | |
| Interest payable | Interest expense is recognised as it accrues. | Interest is payable on Commonwealth Government Securities, swaps and other loans. | |
| International Monetary Fund (IMF) Special Drawing Right (SDR) allocation liability | This liability is recognised as a monetary liability. It is valued at the Australian dollar equivalent of its liability in Special Drawing Rights. Interest expense is recognised as it accrues. | The SDR allocation liability reflects the current value in Aust ralian dollars of the Department’s liability to repay to the IMF Australia’s cumulative allocations of SDRs. Interest is payable to the IMF in relation to the amount of SDR holdings that are below Australia’s net cumulative allocations. |
|
| Provision for unclaimed moneys repayments | A provision is recognised at a nominal value representing the expected recovery of these moneys less refunds already made, based on an analysis of historical transactions. | This comprises moneys which have been paid to the Commonwealth Government as unclaimed moneys in accordance with Section 69 of the Banking Act 1959. These moneys may be claimed by depositors or their legal representatives by applying to the bank concerned. Interest is not paid by the Commonwealth in relation to these moneys. |
Note 30A: Terms, Conditions and Accounting Policies (continued)
| Financial Instruments | Notes |
Accounting Policies and Methods | Nature of underlying instruments |
| Commonwealth Government Securities | Debt is measured at face value. Premiums and discounts in relation to such borrowings are netted and amortised over the life of the borrowing on a straight line basis. | The Department is responsible for advising the Treasurer on all aspects of debt management on behalf of the Commonwealth, including the issue of various borrowing instruments and the administration of the redemption of debt. The Department also administers the redemption of Commonwealth Government security debt on allocation to the States and Territories. | |
| Loans promissory notes | The promissory notes are measured at nominal face value. | The Department has on issue promissory notes to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) and the Asian Development Bank (ADB). These promissory notes are in relation to undrawn paid-in capital subscriptions. Promissory notes to the value of $3,480 million do not possess established drawdown schedules. The promissory notes are non-interest bearing. |
Note 30B: Derivatives Notional Principal Amounts
| (i) Interest Rate Swap Contracts | |||
| The Department has entered into interest rate swap contracts under which it is obliged to receive and pay interest at fixed and/or floating interest rates. | |||
| As at 30 June 1999, the notional principal amounts of the interest rate swaps, which have not been recognised as assets or liabilities, and their associated maturity were as follows: | |||
30 June 1999 |
30 June 1998 |
||
$'000 |
$'000 |
||
| Less than 1 year | 500,000 |
259,501 |
|
| 1 - 2 years | 1,500,000 |
500,000 |
|
| 2 - 3 years | 600,000 |
500,000 |
|
| 3 - 4 years | 2,625,000 |
600,000 |
|
| 4 - 5 years | 2,650,000 |
1,750,000 |
|
| 5 years and over | 9,050,000 |
4,350,000 |
|
16,925,000 |
7,959,501 |
||
| (ii) Cross-Currency Swap Contracts | |||||||
| Swap principal and interest payable/receivable in relation to cross-currency swaps are disclosed in the financial statements on a net basis. | |||||||
| The gross amounts together with their carrying amounts in the financial statements are as follows: | |||||||
Total Carrying |
Gross Amount |
||||||
Amount |
(Cost) |
||||||
30 June 1999 30 June 1998 |
30 June 1999 30 June 1998 | ||||||
$,000 $’000 |
$,000 $’000 |
||||||
| Financial assets | |||||||
| Swaps | 54,810 |
26,899 |
10,301,893 |
11,272,792 |
|||
| Interest receivable Swaps | 43,122 |
62,120 |
196,997 |
349,665 |
|||
148,367 |
89,019 |
10,737,812 |
11,622,457 |
||||
| Financial liabilities | |||||||
| Swaps | 1,396,333 |
2,761,134 |
11,643,416 |
14,007,028 |
|||
| Interest payable Swaps | 10,411 |
22,493 |
164,286 |
310,039 |
|||
1,406,834 |
2,783,627 |
11,996,279 |
14,317,067 |
||||
Note 30C: Foreign Exchange Risk
| The Department is open to foreign exchange risk as a result of contractual obligations in relation to: | ||
| - cross-currency swap contracts; | ||
| - promissory note liabilities in foreign denominations; and | ||
| - foreign currency loans. | ||
| The exposure to the movement in the Australian dollar has not been hedged against. As at 30 June 1999, the following foreign currency assets and liabilities were not hedged: | ||
30 June 1999 |
30 June 1998 |
|
AUD $'000 |
AUD $'000 |
|
| Mon etary liabilities |
||
| Current | ||
| United States Dollars | 207,709 |
1,039,917 |
| Pounds Sterling | 4,639 |
1,517 |
| Hong Kong Dollars |
|
17,021 |
| Euro | 2,570 |
|
| Japanese Yen | 164 |
19,684 |
| Swiss Francs | 50 |
33 |
| Deutsche Marks | 9 |
10 |
| Netherlands Guilders | 62,069 |
95,885 |
| Special Drawing Rights | 5,306 |
7,569 |
282,516 |
1,181,636 |
|
| Non-current | ||
| United States Dollars | 1,714,014 |
2,690,954 |
| Pounds Sterling | 103,404 |
117,646 |
| Euro | 100,000 |
100,000 |
| Japanese Yen | 37,660 |
34,819 |
| Netherlands Guilders | 56,898 |
127,835 |
| Special Drawing Rights | 954,065 |
1,019,157 |
2,966,041 |
4,090,411 |
|
| Total monetary liabilities | 3,248,557 |
5,272,047 |
| Monetary assets | ||
| Current | ||
| United States Dollars | 9,292 |
3,472 |
| Special Drawing Rights | 10,647 |
7,411 |
| Netherlands Guilders | 640 |
3,634 |
20,579 |
14,517 |
|
| Non-current | ||
| United States Dollars | 642 |
|
| Special Drawing Rights | 6,583,265 |
5,053,498 |
6,562,686 |
5,053,498 |
|
| Total monetary assets | 6,583,265 |
5,068,015 |
Note 30D: Interest Rate Exposures The Department’s exposure to interest rate risk and the effective weighted average interest rate for each class of financial assets and financial liabilities is set out below Note 30D: Interest Rate Exposures (continued) Note 30E: Net Fair Values of Administered Financial Assets and Liabilities
Total carrying |
Aggregate net |
||||
Amount |
Fair value |
||||
30 June 1999 |
30 June 1998 |
30 June 1999 |
30 June 1998 |
||
$'000 |
$'000 |
$'000 |
$'000 |
||
| Financial assets | |||||
| Cash | 12,781 |
11,433 |
12,781 |
11,433 |
|
| Interest receivable | 162,781 |
133,640 |
162,781 |
133,640 |
|
| IMF moneys owing | 10,647 |
7,411 |
10,647 |
7,411 |
|
| Swaps | 54,810 |
26,899 |
11,069 |
238,209 |
|
| Loans to State and | |||||
| Territory Governments | 5,783,453 |
7,305,705 |
5,783,453 |
7,305,705 |
|
| Other receivables | 11,817 |
750 |
11,817 |
750 |
|
| Investments | 7,227,042 |
5,717,136 |
7,253,598 |
5,778,053 |
|
13,263,331 |
13,202,974 |
13,246,146 |
13,475,201 |
||
| Financial liabilities | |||||
| Grant liabilities | 25,000 |
27,500 |
25,000 |
27,500 |
|
| Swaps | 1,396,333 |
2,761,134 |
1,390,750 |
2,173,947 |
|
| Interest payable | 2,798,893 |
3,106,480 |
2,798,893 |
3,106,480 |
|
| IMF allocation liability | 954,065 |
1,019,157 |
954,065 |
1,019,157 |
|
| Provision for unclaimed moneys repayments | 48,975 |
41,392 |
48,975 |
41,392 |
|
| Commonwealth Government Securities | 87,693,700 |
96,404,571 |
97,191,300 |
109,744,500 |
|
| Loans promissory notes | 4,346,721 |
3,523,963 |
4,346,721 |
3,523,964 |
|
| Other | 5,332 |
7,569 |
5,332 |
7,569 |
|
97,269,019 |
106,891,766 |
106,761,036 |
119,644,509 |
||
Note 30F: Credit Risk Exposures
| The Department’s exposure to credit risk at reporting date in relation to each class of recognised financial assets is the aggregate net fair value of those assets as indicated in Note 30 (E).
There is no credit risk exposure in relation to the notional principal associated with interest rate swaps. The credit risk associated with Commonwealth Guarantees in respect of authorities within the Treasury Portfolio is shown in Note 16. |
Note 30G: Net Fair Values of Financial Assets and Liabilities
1998-99 |
1997-98 |
|||||
Total Carrying Amount |
Aggregate |
Total Carrying Amount |
Aggregate |
|||
Note |
$'000 |
$'000 |
$'000 |
$'000 |
||
| Departmental financial assets | ||||||
| Cash at bank | 547 |
547 |
36 |
36 |
||
| Receivables for goods and services | 13A |
4,809 |
4,732 |
5,270 |
5,246 |
|
| Total financial assets | 5,346 |
5,279 |
5,306 |
5,282 |
||
| Financial liabilities (recognised) | ||||||
| Finance lease liabilities | 10A |
1,501 |
1,501 |
22 |
22 |
|
| Trade creditors | 11B |
1,126 |
1,126 |
1,044 |
1,044 |
|
| Total financial liabilities (recognised) | 2,627 |
2,627 |
1,066 |
1,066 |
||
| Financial liabilities (unrecognised) | ||||||
| Indemnity on land sale |
|
|
|
|
||
Note 30H: Credit Risk Exposures The Department’s maximum exposures to credit risk at reporting date in relation to each class of recognised financial assets is the carrying amount of those assets as indicated in the Statement of Assets and Liabilities.