List of charts and tables
Charts
International economy
1. Selected international indicators
National accounts
2. Contributions to trend quarterly GDP growth
Tables
National accounts
1. Components of Gross Domestic Product
2. Contributions to change in Gross Domestic Product
3. Gross value-added by industry
Incomes, Costs and Prices
5. Wages, labour costs and company income
6. Prices
External sector
9. Australia's external liabilities
11. Selected economic indicators
Key to tables
n.a. not available
n.y.a. not yet available
.. change less than 0.05 per cent
Chart 1: Selected international indicators
Panel A: Short-term interest rates(a)
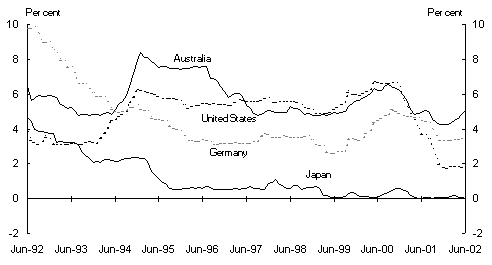
(a) Short-term interest rates are monthly averages and are defined as follows: US - 3 month certificates of deposits, Japan - 3-month certificates of deposit, Australia - 90 day bank accepted bills and Germany - 3 month FIBOR.
Source: OECD Main Economic Indicators.
Panel B: Real output(a)
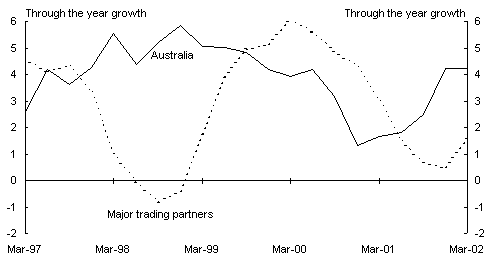
(a) Seasonally adjusted real GDP growth for each major trading partner is weighted by their respective shares of total Australian merchandise exports averaging from 1998-99 to 2000-01. The major trading partners are composed of the OECD and Asian major trading partners. Major trading partners from the OECD comprise the G7 (US, Japan, Germany, France, UK, Italy and Canada) and New Zealand. Asian major trading partners consist of South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Singapore, China, Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand, India and the Philippines.
Panel C: Current account balances(a)
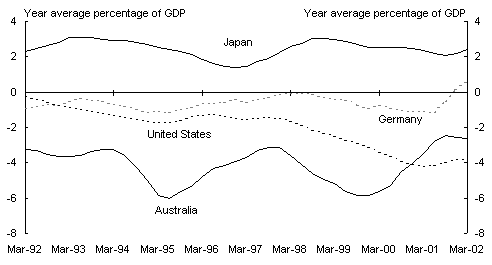
(a) Data are seasonally adjusted. Germany refers to Western Germany until June 1990, and unified Germany thereafter.
Source: Data are sourced from statistical agencies of respective countries, except for data from Germany which is sourced from the OECD Main Economic Indicators.
Panel D: Consumer price inflation(a)
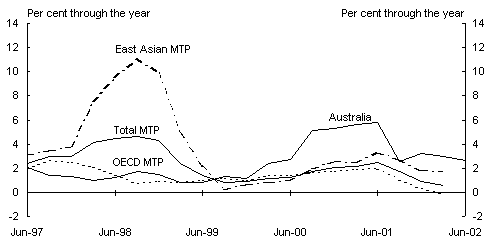
(a) The aggregate inflation rates are derived from the weighted average of inflation rates of individual trading partners, with the weights being their respective shares of Australian total merchandise trade from 1998-99 to 2000-01.
Source: Major trading partners consist of US, Japan, Germany, UK, New Zealand, Canada, South Korea, Singapore, Indonesia, Taiwan, Hong Kong, France, Italy, India, China, Malaysia, Thailand and the Philippines. Data for US, Japan, Germany, UK, New Zealand, Canada, South Korea, Singapore, Indonesia, Taiwan and Hong Kong are sourced from the ABS All Groups CPI (excluding housing) measure. For the rest of Australia's MTP (France, Italy, China, Malaysia, Thailand and the Philippines), the CPI are sourced from each country's respective all groups CPI series which exclude the effects of mortgage interest rate changes.
Chart 2: Contributions to trend quarterly GDP growth
(Chain volume measures)
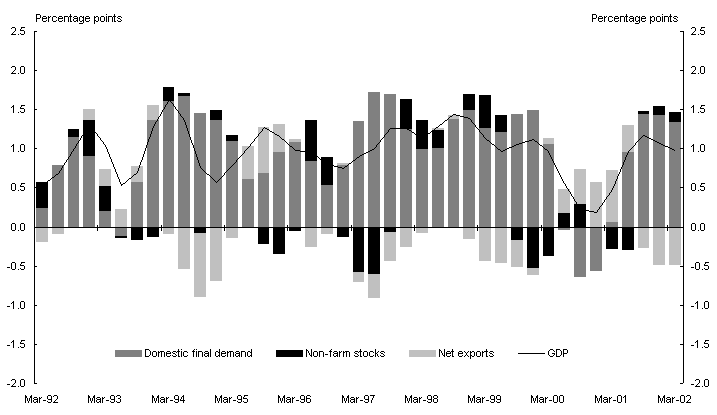
Source: ABS Cat. No. 5206.0.
Table 1: Components of Gross Domestic Product (chain volume measures)
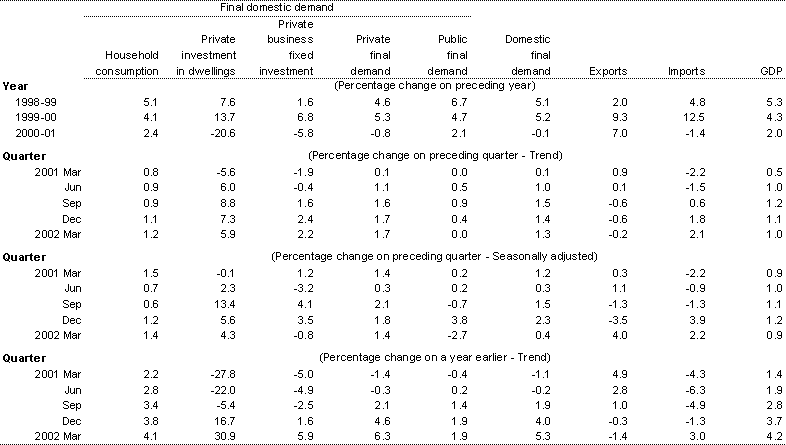
Source: ABS Cat. No. 5206.0.
Table 2: Contributions to change in Gross Domestic Product (chain volume measures)
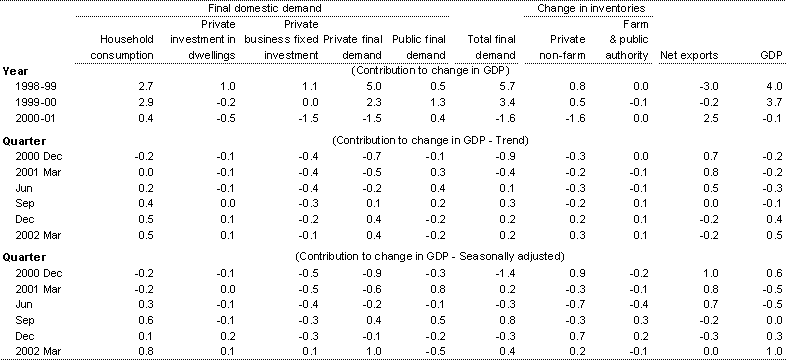
Source: ABS Cat. No. 5206.0.
Table 3: Gross value-added by industry (chain volume measures)
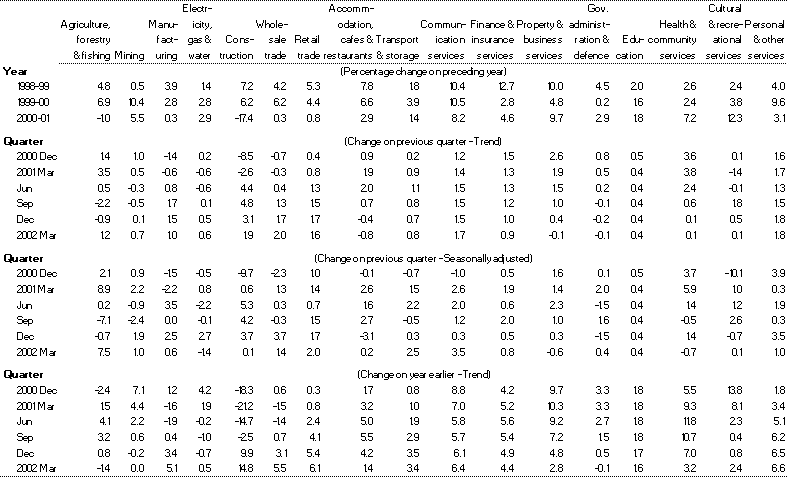
Source: ABS Cat. No. 5206.0.
Table 4: Real household income(a)
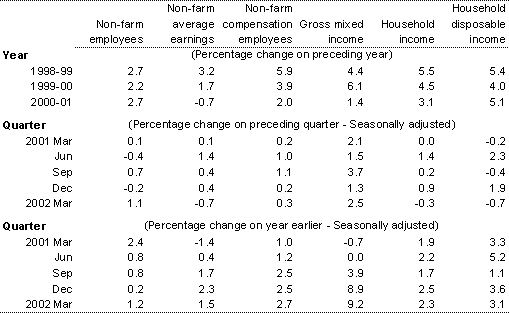
(a) Deflated by the implicit price deflator for private final consumption expenditure.
Source: ABS Cat. Nos. 5204.0 and 5206.0.
Table 5: Wages, labour costs and company income
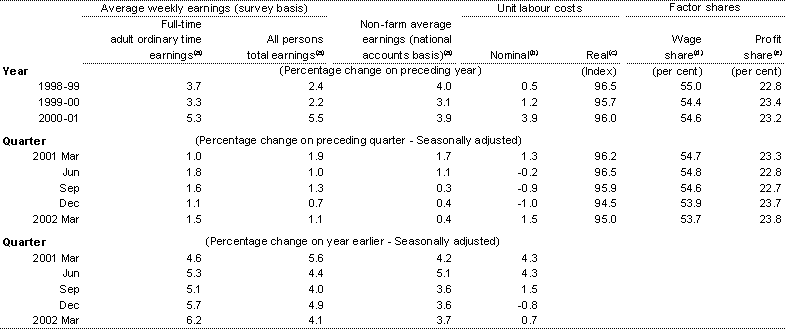
(a) All numbers derived from seasonally adjusted data.
(b) Ratio of nominal hourly labour costs (non-farm compensation of employees, plus payroll tax and fringe benefits tax less employment subsidies, per hour worked by non-farm wage and salary earners) to average hourly productivity (real gross non-farm product per hour worked by all employed persons).
(c) Nominal unit labour costs as defined in footnote (a) deflated by the derived implicit price deflator for gross non-farm product. (Base for index: 1998-99 = 100.0).
Compensation of employees as a share of total factor income.
Gross operating surplus of corporations as a share of total factor income.
Sources: ABS Cat. Nos. 5204.0, 5206.0 and 6302.0.
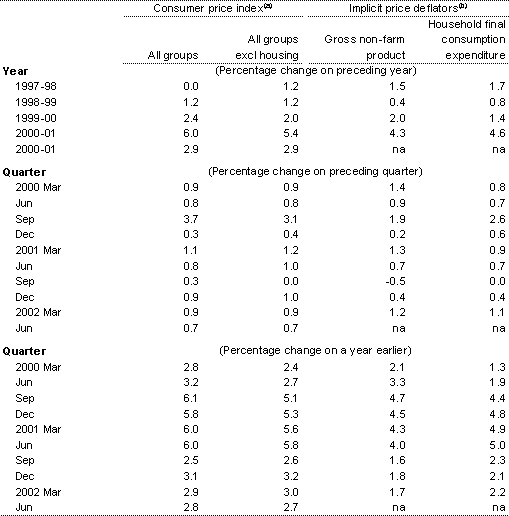
(a) Based on the weighted average of eight capital cities consumer price index.
(b) Quarterly figures are derived from seasonally adjusted data.
Sources: ABS Cat. Nos. 6401.0 and 5206.0.
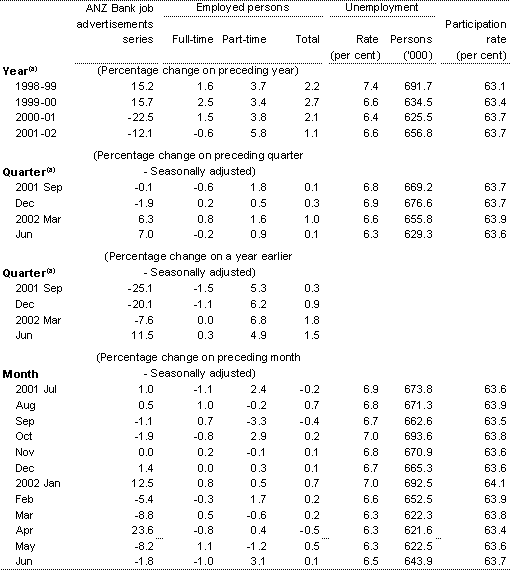
(a) All figures refer to period averages.
Sources: ANZ Bank and ABS Cat. No. 6202.0.
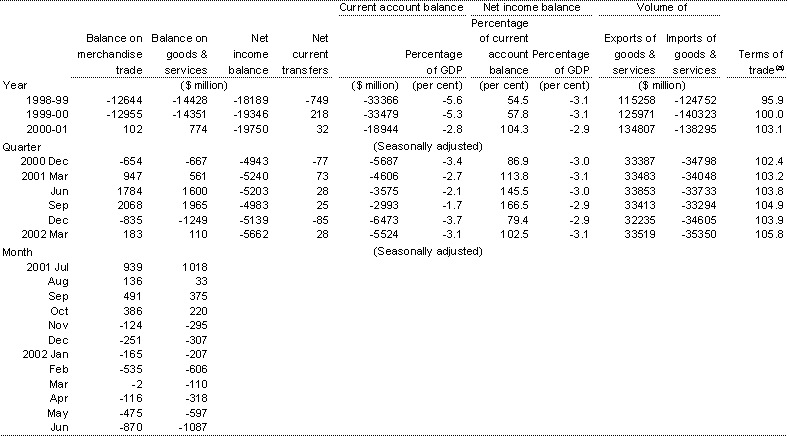
(a) The ratio of the implicit price deflator for exports of goods and services to the implicit price deflator for imports of goods and services, 1998-99 = 100, calculated on a National Accounts basis.
Sources: ABS Cat. Nos. 5368.0, 5302.0 and 5206.0.
Table 9: Australia's external liabilities
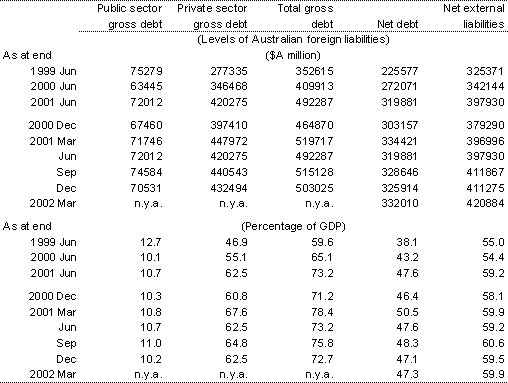
Source: ABS Cat. Nos. 5302.0 and 5206.0.
Table 10: Australia's income flows
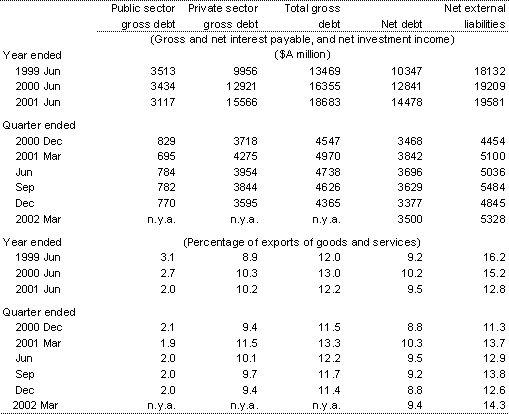
Source: ABS Cat. No. 5302.0.
Table 11: Selected economic indicators
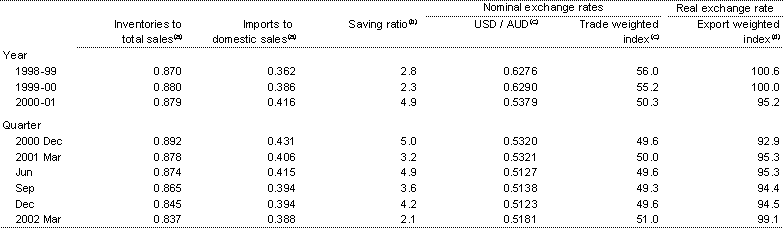
(a) ABS National Accounts measure. All numbers derived from seasonally adjusted data.
(b) Ratio of household saving to household disposable income derived from seasonally adjusted data.
(c) Exchange rates refer to the period average.
(d) Treasury estimate using GDP deflators.
Sources: ABS Cat. Nos. 5206.0, 5302.0.